Wireless sensor data acquisition
Knowledge of simple parameters often has a major impact. If you can now record these parameters easily, it will quickly become economical. With LoRaWAN technology, sensors can be easily and wirelessly installed and integrated into existing systems, for example to record environmental data in production halls and thus gain new insights for quality assurance.
Long ranges with low power consumption
LoRaWAN technology is characterized by long ranges with low power requirements. This means that long-lasting systems can be used to reliably and continuously record data. But what exactly is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network. As the name suggests, it is a radio protocol for covering large areas. It is ideal for small data packets, even over long distances. What's particularly exciting is that it is part of the free network sector. This means that you can set up your own radio network without a lot of bureaucratic effort.
We have illustrated how such a network is usually structured in the following diagram:
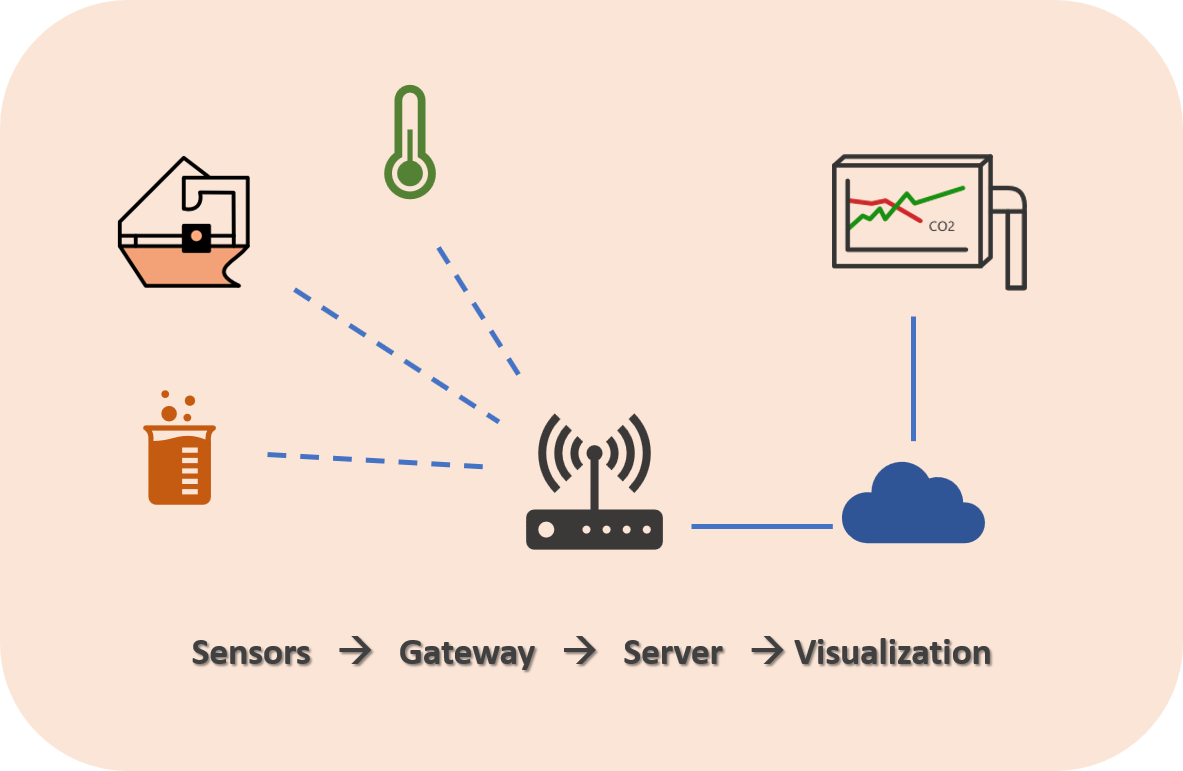
Typical network structure of a LoRaWAN
The sensors are installed on site in their area of responsibility and send the data wirelessly to a gateway. This gateway receives the data and forwards it to a server, whether on site or in the cloud. This means that if the gateway is connected to the cloud, it must be connected to the internet. In some cases, the gateways may also cumulate the data via a collection point, such as an edge gateway. From the server, the data is either sent to existing monitoring systems or displayed directly via web applications so that it can be analyzed visually.
What are typical example applications?
Typical example applications for these sensors are the recording of environmental factors and data, such as air temperature, CO2 utilization in a room, humidity measurement and water meter monitoring. The recording and automated evaluation (e.g. threshold value exceedance) is carried out optimally and quickly with this technology.
The charming thing is that if you already have an existing LoRaWAN network, more and more sensors can be integrated with very little effort. It is already known that water meters and electricity meters will increasingly be equipped with LoRaWAN interfaces in the future. This results in a very simple example in which a rapid amortization can be seen. By installing a water meter with LoRaWAN, you can find out much more quickly whether a toilet flush is still running due to limescale and can react more quickly. Even without reading the daily consumption manually from the water meter every day.
Frequently asked questions about LoRaWAN
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a radio protocol in the field of free networks. It is particularly suitable for the transmission of small data packets, such as temperature or humidity, even over very long distances. However, the power requirement increases as the transmission distance increases.
How far can you cover distances with it?
We have covered ranges of over 7 km in our own tests and were still able to receive data. On the Internet you often read about ranges of up to 10 km. However, this depends very much on the topography and landscape structure. For example: Are there large reinforced concrete structures between the sensor and the gateway?
Can I also use it to record other data?
Of course, the number of use cases is huge. As no cable connection is required, this technology can be used to track locations in certain areas. Example: Is “carrier trolley A” currently located in “warehouse building 1” or in “warehouse building 2”? A simple check-in/check-out system is implemented for this purpose.